Since Robotic process automation and other forms of automation caught the imagination of people, there have been efforts to go beyond the limited rule-based automation. Intelligent Automation (IA) is one of the terms used to describe a new and enhanced automation by adding AI technologies.
In this post, we will do a deeper dive into Intelligent Automation and go over a few real-world examples to help you understand what intelligent automation can do for you.
Let’s start with a quick introduction to Intelligent Automation.
What is Intelligent Automation
Usually, anything with Artificial Intelligence (AI) is considered intelligent, or smart.
For example, Intelligent ERP is AI combined with ERP. Let’s take the example of SAP. They call SAP S4 / HANA with embedded AI as Intelligent ERP.
So you guessed it – AI plus Automation is what is generally called Intelligent Automation.
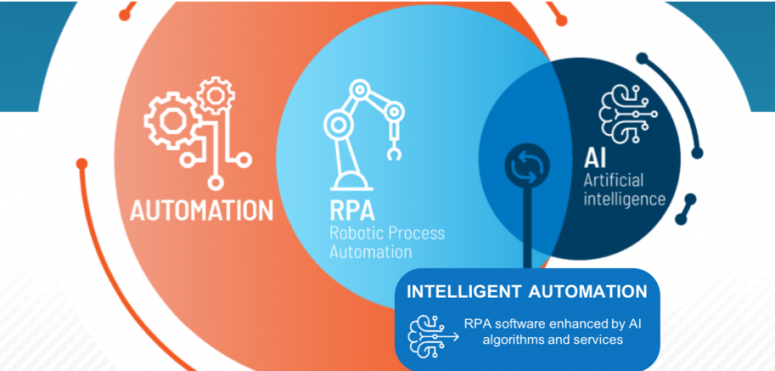
Now, the automation itself can use many technologies. The usual contenders include Robotic process automation (RPA) and Digital process automation (DPA). It can also be, other Low-code or No-code automation technologies. You can even use code-based automation like Python!
Even the AI technologies used for automation come in different flavors. For e.g., it can be Machine learning (ML), Natural language processing (NLP), Computer vision (CV), and more.
So, there you have it – various Automation and AI technologies combine to form Intelligent Automation. But, do we have a clear cut definition?
Intelligent Automation definition
There are a few definitions about Intelligent Automation terms from various sources including IEEE 2755. Here is a definition from the Intelligent Automation book:
IA, also called Hyperautomation, is a concept leveraging a new generation of software-based automation. It combines methods and technologies to execute business processes automatically on behalf of knowledge workers. This automation is achieved by mimicking the capabilities that knowledge workers use in performing their work activities (e.g., language, vision, execution, and thinking & learning). The goal of using IA is to achieve a business outcome, through a redesigned automated process, with no or minimal human intervention. As a result, IA increases process speed, reduces costs, enhances compliance and quality, increases process resilience, and optimizes decision outcomes. Ultimately, it improves customer and employee satisfaction and boosts revenues.
Intelligent Automation
Pascal Bornet, Ian Barkin, and Jochen Wirtz
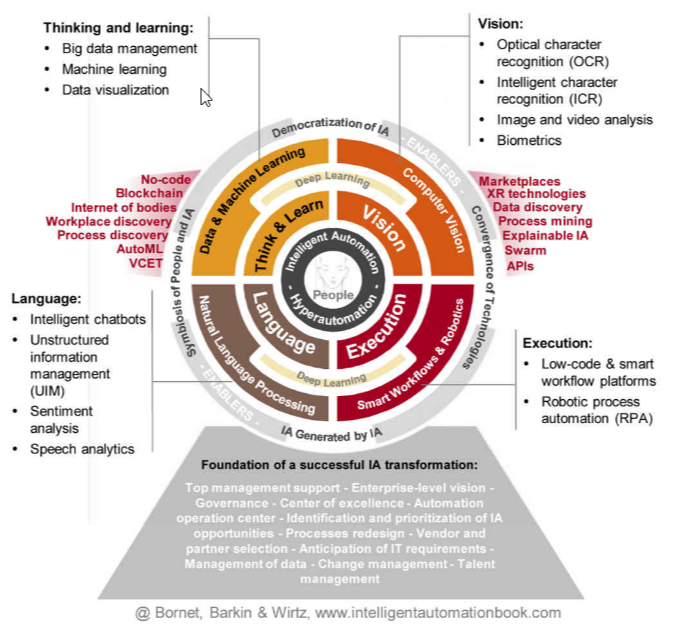
As you can see RPA is one of the technologies that enable Intelligent Automation. How do they differ?
Intelligent Automation and RPA
What is the difference between RPA and intelligent automation? Is RPA intelligent automation?
No RPA is NOT Intelligent Automation (IA) but RPA certainly has played a part in the evolution into IA or Hyperautomation. Software-based Automation is much more than RPA or AI or any single technology though.
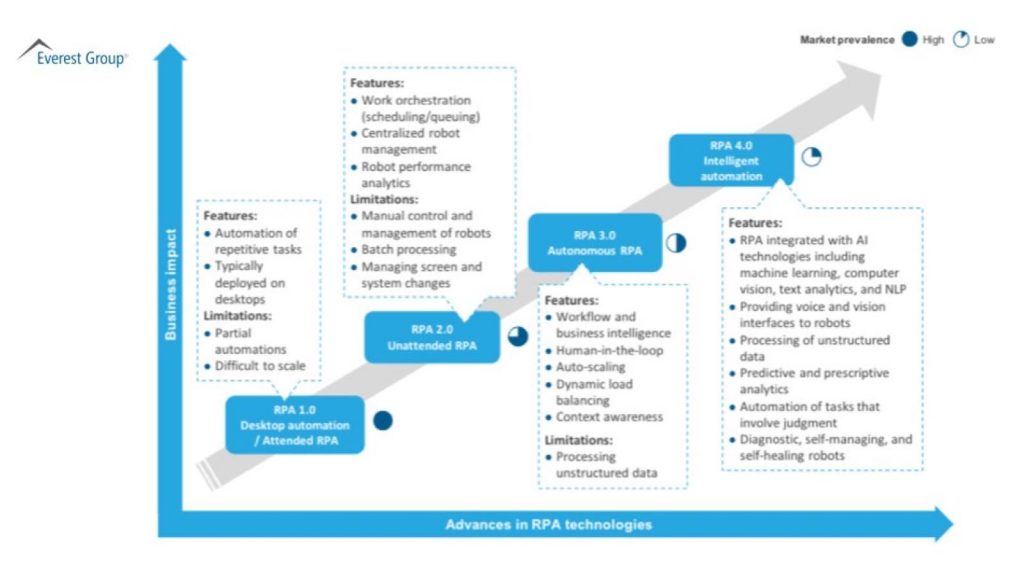
Since Intelligent Automation or RPA 4.0 as Everest calls it above, is mostly about adding AI, to automation, what are the AI technologies used for automation?
AI Technologies in Intelligent Automation
Here are the key AI technologies currently used within automation:
- Natural Language Processing: It helps with the understanding the meaning and intention of sentences through machine learning and statistical methods.
- Computer Vision: This form of AI is used to extract, analyze and understand information from images e.g. Scanned documents.
- Machine Learning: These are algorithms that improve automatically “learns” to detect patterns and predict outcomes with help of data.
These AI expands the scope of what we can Automate. Let’s take a look at a few real-world examples to understand what we can do with Intelligent Automation.
Let’s start with a common use case – Invoice Processing.
Intelligent Automation Examples
Invoice processing
As we know, in a manual invoicing process, customers receive an invoice from the supplier. The invoice is input into the accounting software generally using copy-paste. Then the invoice is sent for approvals, and once approved, the payment is made.

Now, automation tools like RPA can automate a major part of this process. RPA can extract the invoice data and verify the invoices. It can then input the data into the accounting system for approvals and payment.
Since RPA is rule-based, its data extraction capability is quite limited. The computer has to be told to look for a text anchor or look for a position and extract the required values.
Now, This is okay, as long as we only have a few Invoice formats to process. In the real world though, there are many formats that each customer receives. For example, one of my customers has got 4000 plus formats. So, it becomes tedious to do this rule-based mapping for each invoice.
Instead, what if the machine could learn the mapping by itself? That’s what artificial intelligence for AI enables for us. It uses a combination of AI techniques to map the fields. The AI techniques used include computer vision (CV) and Machine learning (ML).
The AI extracts the data and presents its mapping to us. We can then correct the mappings it could not get right. It learns in the process and improves over a period of time. AI thus does a bulk of the work rather than you mapping each template, one by one.
Once AI does the bulk of the work, we can combine that AI output with RPA to get to a higher data extraction accuracy. RPA can also input this data into your accounting systems or ERP.
So, as you can see, RPA with added AI intelligence improves automation quite a lot. Here is a demo.
Now, AI can do more than this, as we’ll see in our next Automation use case – Claims Processing.
Claims Processing
Next, we’ll see how we can automate Vehicle claims with Automation.

Usually, after a vehicle accident, customers have to file a claim with damage details. This is a manual process that takes days to process.
We can automate this process using a Chatbots, RPA, and Google damage assessment API.
A chatbot collects the details of the claim including the damaged vehicle photographs. An RPA bot then matches the submission to policy details. It invokes the a damage assessment API to assess the damage. Finally, it provides a claim number to the user via chat.
We can see that with more AI capabilities, you can do more! We can string more AI and Automation tools to create more complex automation. We will look at one such use case next – Customer onboarding.
Customer Onboarding
Let’s see how software-based automation can transform an Onboarding process. This is an example from the Intelligent automation book.
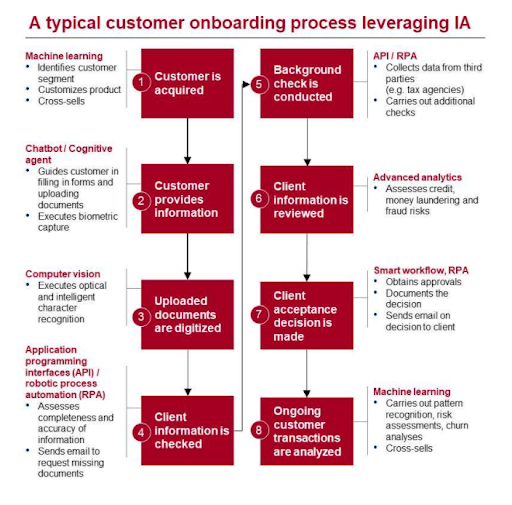
When a customer is acquired, we can use Machine learning to segment them. We can then use a Chatbot to have customers provide their information. They usually submit a few documents which can be digitized with AI.
RPA can help us check if there is any missing information, and reach out to the customer to get that information. Once we have all the information, RPA can do background checks and use AI to detect any fraud. Finally, we can keep monitoring the customer data for any churn risk or even for any cords sell opportunities.
So we can see how Intelligent Automation (IA) can transform your customer onboarding process. This is just another example. You can use IA to transform multiple processes in your organization.
Looking forward – Intelligent Automation
Organizations are moving to the next stage of Software-based automation by adding aspects of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to their Automation initiatives. As per Deloitte, Organizations that scale are more likely to use a combination of RPA and AI. They see that almost half (45 per cent) of organizations scaling automation by combining RPA and AI.
Organizations that are using AI along with RPA are not only likely to scale better but they also report the Automation initiatives meets or exceeds their expectations. They also report higher revenue increases and enable more gains in workforce capacity.
Bottom-line is that you stand to gain a lot more scale and benefits by using Intelligent Automation.
Before we go, here is a video with this and more.